
In my professional practice, six main levers for R&D performance have proven their worth:
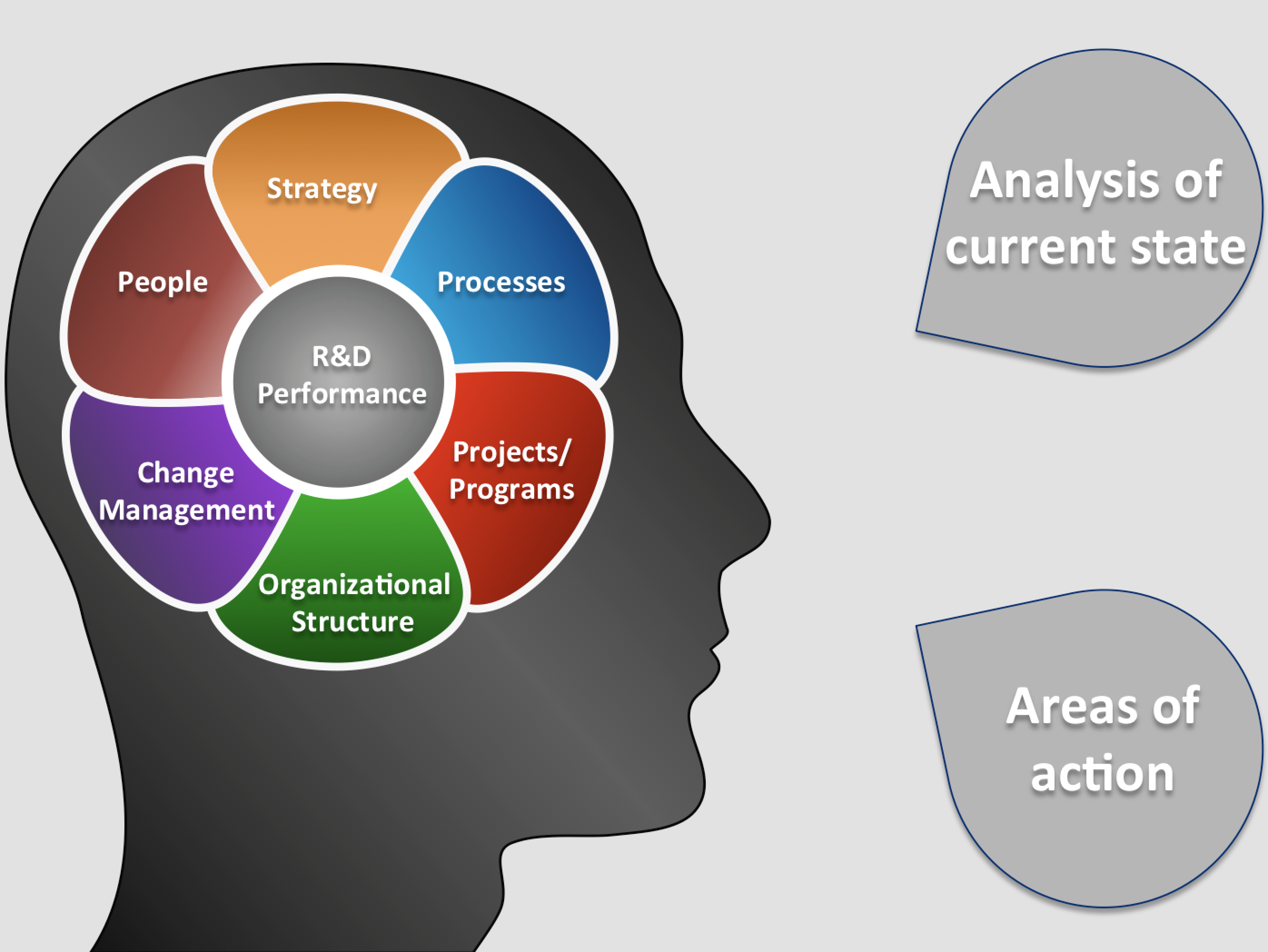
Of course, it is not surprising that these factors are also found in many places in the well-known quality management systems such as ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (medical devices).
According to these levers, an analysis of the actual state can be perforemd and weak points can thus be identified. In addition to this internal absolute view of the current state, external benchmarking can also be carried out via competitive comparisons (relative external view).
First of all, it is important to ensure that the R&D strategy is suitably integrated into the corporate strategy and supports it optimally. This essentially determines effectiveness ("doing the right things").
R&D processes describe the standardized procedures in the various lifecycle phases (research, technology development, series development, product maintenance) of a product or service. This decisively determines efficiency ("doing things right"). An important point here is that the development process is a corporate process and should not be understood as a pure "technology event".
R&D project and program management determines the operational implementation of the strategy in the form of a project portfolio. Important topics that strongly influence efficiency here are project organization and the composition of the (interdisciplinary) project teams. Depending on the specific situation, classic, agile or hybrid project management is recommended.
The R&D structure is usually organized functionally according to specialist competencies. However, a matrix structure is often recommended, e.g., to support efficient project implementation in addition to promoting technical synergy effects. It is optimal if the organizational structure supports the operational structure (processes) and avoids obstructive interfaces.
In order to sustainably implement potential changes in the R&D system, these must be accompanied by appropriate change management.
As in many other areas, the people involved - managers and employees - play a decisive role in operational implementation due to their individual personalities and competencies. Therefore, looking closely at the people involved is an integral part of my approach.
In addition to the six factors mentioned above, the company's vision, mission and values naturally also influence R&D performance. A good R&D leader will refer to this and explain the stable presence and the better future to the employees and always lead by example.
In summary, I can say that by analyzing the six levers, an initial overview of the most important R&D action areas can be quickly created. After prioritization, one can then create the implementation roadmap.
If requested, I am happy to be available as an interim manager during the implementation.